
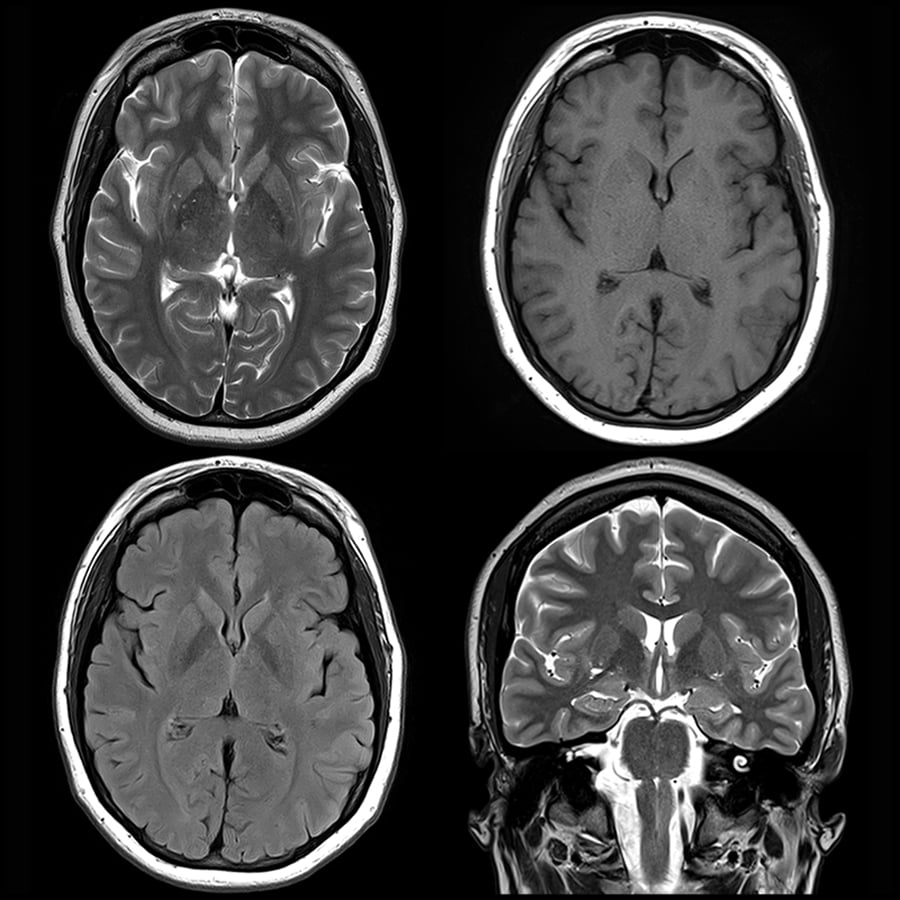
In healthy adult volunteers, the scanner can generate T1-weighted, T2-weighted and proton density-weighted brain images with a spatial resolution of 2.2 × 1.3 × 6.8 mm 3. MRI provides better soft tissue contrast than CT. Imperfections in the encoding fields are mitigated with a generalized iterative image reconstruction technique that leverages previous characterization of the field patterns. An MRI scanner can be used to take images of any part of the body (e.g., head, joints, abdomen, legs, etc.), in any imaging direction. The built-in magnetic field gradient reduces the reliance on high-power gradient drivers, lowering the overall requirements for power and cooling, and reducing acoustic noise. The 122-kg low-field (80 mT) magnet has a Halbach cylinder design that results in a minimal stray field and requires neither cryogenics nor external power. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a test that uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to make pictures of the organs and structures inside. MRI uses a magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to create images soft tissues, bones, and internal body structures. An MRI creates clear images of brain tissue.
#Mri of the brain portable
Here, we report the design and testing of a portable prototype scanner for brain MRI that uses a compact and lightweight permanent rare-earth magnet with a built-in readout field gradient. The doctor may order a brain scan to make sure you do not have a fractured skull or a serious brain injury.

Access to scanners for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is typically limited by cost and by infrastructure requirements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
